Introduction: Python IDLE Explained
If you have recently installed Python on your system, there is a very high chance that you already have a tool to write and run Python code — without installing any extra software. That tool is called Python IDLE.
Most beginners jump directly to modern IDEs like PyCharm and completely miss Python IDLE. As a result, they never clearly understand how Python actually runs code, what an interpreter is, or how Python works behind the scenes.
In this detailed PyCoderHub guide, you will learn:
- What Python IDLE is and why it comes with Python
- How to open, use, create, and modify files in IDLE
- How to write Python code using Command Prompt (CMD)
- How to write and run Python code using Notepad
- A comparison of all options
- Why PyCharm is still the best choice for beginners
What Is Python IDLE?
Python IDLE (Integrated Development and Learning Environment) is the official Python editor that comes automatically with every Python installation. It provides a beginner-friendly platform to write, test, and run Python code without installing any extra software.
Python IDLE is mainly designed for:
- Writing and executing Python scripts quickly and easily
- Learning Python through its interactive shell
- Testing small code snippets without creating full projects
- Simple debugging with basic error messages and tracebacks
- Understanding Python syntax with highlighted code
Note: Python IDLE is not a separate download—it’s included with Python itself, so once you install Python, you already have this editor ready to use.
Does Python Come with IDLE by Default?
Yes! Python comes with IDLE by default, which means you don’t need to download or install it separately. When you install Python on Windows, macOS, or Linux, IDLE is automatically included as part of the standard Python package. This makes it incredibly convenient for beginners who want to start coding immediately without setting up additional software.
Key points to know:
- IDLE is pre-installed with Python on all major operating systems.
- You can access it directly from your Start Menu (Windows), Applications folder (macOS), or by running
idlefrom the terminal on Linux. - Being bundled with Python ensures that IDLE is always compatible with the version of Python you are using.
- It’s perfect for learning Python, testing scripts, and quick experimentation before moving to more advanced IDEs like PyCharm.
Note: Even though IDLE comes with Python by default, some users might skip installing optional components during setup. If you’re unsure, you can check out our previous guide on how to install Python correctly to make sure everything is set up properly.
Key Features of Python IDLE
Python IDLE may look simple, but it comes with several useful features that make coding easier for beginners and quick testing faster for all users. Here are the key features that make IDLE a reliable choice:
- Interactive Python Shell: Execute Python commands line by line and see immediate results, perfect for experimenting and learning.
- Code Editor with Syntax Highlighting: Makes Python code more readable and helps spot errors quickly.
- Basic Debugging Tools: Includes a debugger with breakpoints, step-through execution, and error messages to help troubleshoot code.
- Auto-Completion: Suggests variable names, functions, and keywords as you type, saving time and reducing mistakes.
- Multi-Window Editing: Allows working on multiple scripts simultaneously for better project management.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux, just like Python itself.
- Lightweight and Fast: Opens quickly without the heavy resource usage of full-featured IDEs.
Note: While IDLE is beginner-friendly and great for learning, small projects, and testing snippets, it doesn’t include advanced features like version control integration or complex project management found in modern IDEs such as PyCharm.
How to Open Python IDLE
Accessing Python IDLE is simple, and the steps differ slightly depending on your operating system. Here’s how you can open it on Windows, macOS, and Linux:
On Windows:
- Press the Start Menu and type IDLE or Python IDLE.
- Click IDLE or Python IDLE from the search results.
On macOS:
- Open the Applications folder.
- Locate the Python 3.x folder.
- Double-click IDLE to launch the editor.
- Alternatively, you can open Terminal and type:
idle3
On Linux:
- Open your terminal.
- Type
idleoridle3(depending on your Python version). - Press Enter to open IDLE.
- Some Linux distributions also include IDLE in the application menu under Programming or Development.
Tip: You can also create a desktop shortcut for IDLE on Windows or macOS to launch it even faster.
Writing Python Code Using IDLE
Writing Python code in Python IDLE is straightforward, making it an excellent choice for beginners who want to focus on learning the language rather than configuring tools. IDLE offers two main ways to write and run Python code.
- Using the Interactive Shell
- Using the Script Editor
1. Using the Interactive Shell
When you open IDLE, the Python Shell appears by default. This allows you to type Python commands and see the output immediately. See the image below:
This is where you type and execute code line by line. Try typing the code below in IDLE:
#Press enter after typing code for output
>>> print("Hello, Python!")
Hello, Python!
>>> 10 + 20
30
>>> for i in range(3):
print('PyCoderHub')
PyCoderHub
PyCoderHub
PyCoderHubBelow is an image showing how it looks in IDLE:
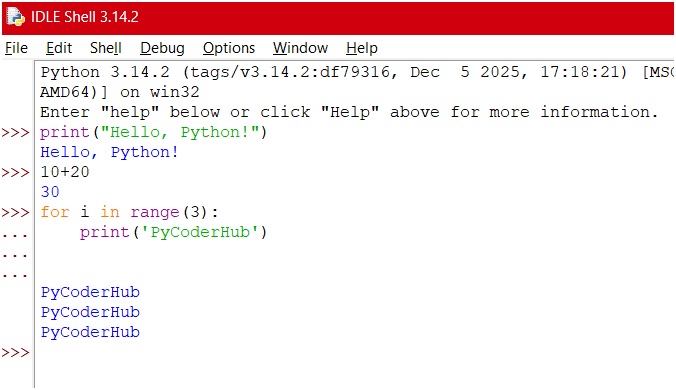
Every time you press Enter, IDLE runs the code and shows the output instantly. This is perfect for testing or learning new syntax quickly.
2. Using the Script Editor (File Mode)
For writing full programs, IDLE provides a script editor.
Creating a New Python File in IDLE
To open the editor:
Click File → New File
A new blank window appears — this is where you’ll write your script.
Example:
# pycoder.py
print("Welcome to PyCoderHub")
name = input("Enter your name: ")
print("Nice to meet you,", name)Now save your file:
- Click File → Save As…
- Choose a location (e.g., Desktop)
- Name it
pycoder.py - Click Save
Note: You don’t need to write
.pyafter the file name. By default,.pyis automatically added because it is the Python file extension.
To Run This Code:
Press F5 or go to Run → Run Module
You’ll see the output in the Python Shell.
Editing and Saving Files in IDLE
Once you’ve created a file:
- You can edit it anytime by reopening the file from File → Open → Select your file.
- Make your changes, then press Ctrl + S to save.
Example: Updating the previous saved file
# pycoder.py
print("Welcome to PyCoderHub")
name = input("Enter your name: ")
print("Nice to meet you,", name)
print("Now you are learning Python IDLE")Save and press F5 to run again.
That’s how you can write and run Python code using Python IDLE. It’s simple, beginner-friendly, and perfect for learning and quick testing. Now, let’s move on and see how we can run basic Python code using the Command Prompt (CMD).
Running Python Code Using Command Prompt (CMD)
Now that you understand how Python IDLE works, it’s important to know that you can also run basic Python code directly using the Command Prompt (CMD). This method is widely used by developers and helps you understand how Python actually runs behind the scenes—without any graphical editor.
Using CMD is especially useful for verifying Python installation, running scripts quickly, and executing Python commands inline.
1. Check Python Installation in CMD
Before running any code, you should confirm that Python is properly installed on your system.
Open Command Prompt and type:
python --versionIf Python is installed correctly, you’ll see the installed Python version.
If not, CMD will show an error, which usually means Python is not installed or not added to the system PATH.
2. Open Python in Interactive Mode
You can start Python’s interactive shell directly from CMD by typing:
pythonThis opens interactive mode, where you can execute Python commands line by line.
Example:
print("Python is running in Command Prompt")You’ll see the output immediately. The image below shows the Python output in the Command Prompt:
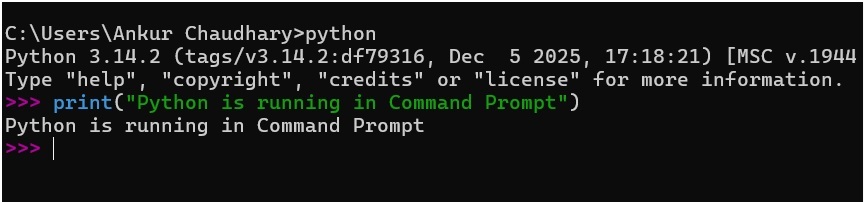
To exit interactive mode, type:
exit()3. Run a Python File Using CMD
CMD is commonly used to run saved Python scripts.
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt
- Navigate to the folder where your Python file is saved using
cd - For example, if your file
PyCoder.pyis on your desktop: - Run the file using the
pythoncommand
Example:
cd desktop
python pycoder.pyBelow is an image showing how this code looks when run in CMD.
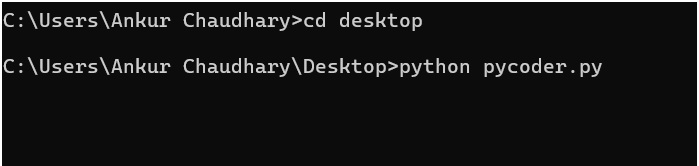
The output of the program will appear directly in the Command Prompt window.
4. Run Inline Python Commands in CMD
You can also execute single-line Python commands without entering interactive mode by using the -c flag.
python -c "print('Running Python inline from CMD')"This is useful for quick checks, automation, and testing small logic.
Note: The
-cflag allows you to run Python code directly from the Command Prompt without creating a.pyfile. It is best suited for quick tests, small commands, or one-line scripts, rather than full Python programs.
Writing Python Code in Notepad
So far, we’ve seen how to use Python IDLE and how to run Python code using Command Prompt (CMD). But did you know that you can even write Python code in a simple text editor like Notepad? Yes—Python doesn’t require a special editor to write code. Any plain text editor can be used as long as the file is saved correctly.
Notepad is a very basic option and doesn’t provide features like syntax highlighting or error checking, but it helps beginners understand an important concept: Python code is just plain text.
Steps to Write Python Code in Notepad
1. Open Notepad
2. Write your code:
print(“Running Python from Notepad!”)
3. Save as:
File → Save As
4. Change Save as type to All Files.
5. Save the file with a .py extension (for example, example_script.py).
Once saved, you can run this file using Command Prompt (CMD) with the python command, just like we did earlier in the “Run a Python File Using CMD” section.
Note: When saving a Python file in Notepad, always make sure to use the
.pyextension. Without it, the file won’t be recognized as a Python script and cannot be executed using thepythoncommand.
Different Ways to Write Python Code
In this post, we learned about different approaches to writing Python code, each suited for a specific learning stage or use case:
- Python IDLE – Simple and beginner-friendly
- Command Prompt (CMD) – Direct interaction with Python
- Notepad – Pure understanding of Python scripts
- PyCharm – Full-featured modern IDE (learned about PyCharm in a previous chapter)
Here, we’ll focus on comparing it with the other methods to help you choose the right tool for your needs.
Comparison: Python IDLE vs CMD vs Notepad vs PyCharm
| Feature | IDLE | CMD | Notepad | PyCharm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Friendly | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Syntax Highlighting | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Error Detection | Basic | None | None | Advanced |
| Debugging Tools | Basic | No | No | Powerful |
| Project Support | No | No | No | Yes |
| Comes with Python | Yes | Yes (OS default) | Yes (OS default) | No |
| Best Use Case | Learning & small scripts | Running scripts & testing | Understanding .py files | Professional development |
Why PyCharm Is a Better IDE for Beginners
So far, we’ve covered different ways to write Python code, explored multiple approaches, and compared tools like IDLE, CMD, and Notepad. Now the natural question is: why is PyCharm often considered a better IDE for beginners?
PyCharm is a modern, full-featured Python IDE developed by JetBrains. While it may look advanced at first, PyCharm is designed to guide beginners, reduce errors, and make Python development more structured and productive as projects grow.
Beginner-Friendly Features of PyCharm
- Smart Code Editor: Provides intelligent code completion, suggestions, and error highlighting while you type.
- Clear Error Messages: Explains mistakes in a beginner-friendly way, helping you fix issues faster.
- Built-in Debugger: Lets you step through code line by line and understand how Python executes.
- Project-Based Structure: Helps beginners learn how real Python projects are organized.
- Integrated Run & Terminal: Run Python scripts with one click and access the terminal without leaving the IDE.
- Syntax Highlighting & Formatting: Makes code more readable and easier to understand.
- Virtual Environment Support: Automatically manages Python environments, reducing setup confusion.
Why beginners eventually prefer PyCharm:
- Less confusion as projects grow
- Fewer runtime errors due to early detection
- Encourages best coding practices from the start
Note: PyCharm may feel overwhelming at first, but once you understand the basics, it becomes one of the most powerful and beginner-supportive tools for learning Python effectively.
Conclusion
Python offers multiple ways to write and run code, including IDLE, Command Prompt, Notepad, and PyCharm, each serving a different purpose. Python IDLE is ideal for beginners who want a simple and distraction-free environment, while CMD helps you understand how Python executes scripts behind the scenes. Notepad teaches the basics of working with Python files, and PyCharm provides a full-featured IDE for building real-world projects. As you progress, moving from basic tools to a professional IDE like PyCharm will make your Python development more efficient and structured.
Suggested Posts:
1. What is Python? The Ultimate Guide for Beginners (2026)
2. The Evolution and History of Python: From Hobby Project to Global Dominance (1989–2026)
3. Understanding Python Programming Terms: High-Level, Interpreted, Garbage-Collected Explained
4. How to Install Python and Set Up PyCharm (Beginner’s Guide)
5. Python Introduction FAQs: Common Beginner Questions Answered


2 thoughts on “Python IDLE Explained: Comparison with PyCharm, CMD, and Notepad”